12.32 When viewed graphically, each node in a 2-d tree partitions the plane into regions.
For instance, Figure 12.51 shows the first five insertions into the 2-d tree in
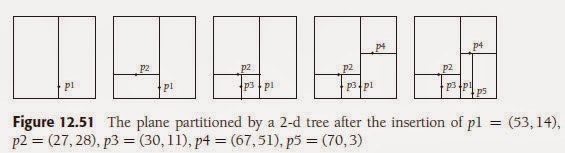
Figure 12.39. The first insertion, of p1, splits the plane into a left part and a right part. The second insertion, of p2, splits the left part into a top part and a bottom part, and so on.
a. For a given set of N items, does the order of insertion affect the final partition?
b. If two different insertion sequences result in the same tree, is the same partition
produced?
c. Give a formula for the number of regions that result from the partition after N
insertions.
d. Show the final partition for the 2-d tree in Figure 12.39. -